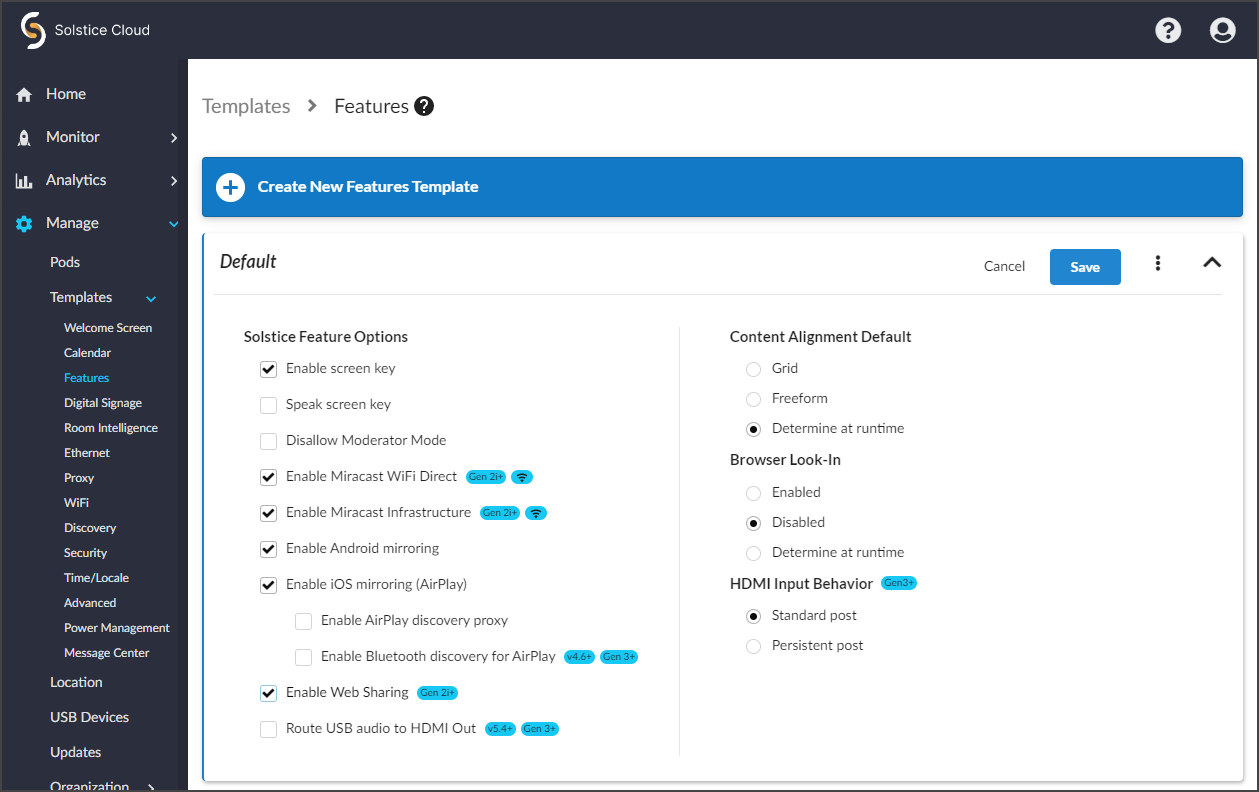
Features Template
The Features template allows you to configure options for how attendees view and interact with the Solstice display. It includes options that determine how attendees can connect to the meeting, as well as how they view and share content on their personal devices. Miracast and AirPlay support can also be enabled. For more information on how to configure Solstice to support sharing with AirPlay and Miracast, see Enable Sharing with AirPlay and Enable Sharing with Miracast.
How To
Note
Want to enable Solstice video conference connections or occupancy data? See the Room Intelligence TemplateRoom Intelligence Template.
Next Topic
Enable Sharing with Miracast
Screen mirroring for Windows devices is available through Solstice's support for Miracast streaming. This allows users to wirelessly mirror or extend their screen to the Solstice display in real-time without having to install an app.
Solstice's support for Miracast works in two stages. In the discovery stage, a Miracast-enabled device searches for active Miracast receivers nearby for the user to connect and stream to. This requires the Solstice Pod’s wireless network interface card to be enabled and not acting as a wireless access point. In the second stage, the device streams content to the Miracast receiver using either an existing network (Miracast over Existing Network) or a peer-to-peer wireless connection (WiFi Direct).
Solstice's Miracast support has three modes:
Over Existing Network/Infrastructure and WiFi Direct (recommended). Allows Pods to dynamically select best video streaming mode. Most robust device connection and setup configuration. Windows and Android devices supported.
Over Existing Network/Infrustructure. Leverages existing network to support larger number of simultaneous Miracast users. All Miracast traffic is subjected to network security and monitoring. Windows 10 and later devices supported.
WiFi Direct. Good for use cases where one Miracast device is used at a time. Windows and Android devices supported.
Network Routing Requirements
The following network ports/routes are required to support Miracast streaming to Solstice Pods.
TCP port 7236: WiFi Direct control port used to establish and manage sessions between the source device and the Pod.
TCP port 7250: Port on which the Pod listens for Miracast packets when Over Existing Network mode is enabled.
UDP port 5353: If Miracast Over Existing Network mode is enabled, this port is used for multicast DNS (mDNS). mDNS is broadcast to the local subnet of each network interface the Pod is connected to. If the computer that is attempting to make an infrastructure connection is on a different subnet, this broadcast will fail. If this happens, a workaround is to create a DNS entry to the Pod’s hostname.
For for Gen2i Pods, confirm that port 32768:60999 is also open.
Ensure that the IP address space for WiFi Direct (192.168.49.*) is not behind a firewall.
Note
Miracast may use any non-privileged UDP port from 1024 to 65535 for video streaming.
Important Considerations
Miracast requires that the Pod be located in close proximity to the display. Miracast discovery operates over a range of approximately 150–200 feet. Only Pods within this range appear in the Miracast source list on the client device.
Many factors can affect the performance of Miracast streaming. For more information on Miracast performance by configuration and use case, view the Miracast Performance Tech Note.Miracast Performance Tech Note.
How To Enable Sharing with Miracast in Solstice Cloud
Log in to Solstice Cloud. In the left sidebar navigation, expand the Manage category and select Pods.
From the table, click the name of the Pod to be set up for Miracast. Scroll down to Template Configuration section and apply the following settings, according to your network configuration based on the table below.
Pod's Network Configuration
Pod Configuration for Miracast in Solstice Cloud
Ethernet Only (recommended)
Expand the WiFi settings. Select Enable WiFi, choose Existing Network, and set Security Type to Open. This enables the wireless antenna for Miracast discovery. Do not enter an SSID to attach the WiFi interface to an existing network. This interface remains idle and is used for the Miracast discovery stage. Use one of the Save options (see step 3 for details) to update the Pod.
Expand the Features settings and select Enable Miracast Infrastructure and Enable Miracast WiFi Direct.
Wirelessly Attached to Existing Network Only
Select Enable Miracast Infrastructure.
Ethernet + Wirelessly Attached to Existing Network
Select Enable Miracast Infrastructure.
Ethernet + Wireless Access Point
Miracast not supported. When the Pod is acting as an access point, Miracast discovery cannot operate. Contact Mersive to discuss other options like attaching your Pod to an existing network.
Wireless Access Point Only
Save the Miracast settings changes with the option that best fits your situation:
Click Save as Unassigned to save the Pod's Features settings uniquely (not assigned to a template).
Click Save as New Template to create a Miracast-enabled Features template that other Pods can be assigned to in the Pods table.
How To Enable Sharing with Miracast in Solstice Dashboard
Open Solstice Dashboard on a Windows computer. Select the Pod to be set up for Miracast from the list of Your Solstice Instances.
Find the Pod's network configuration in the table below and apply the corresponding configuration in the Solstice Dashboard.
Pod's Network Configuration
Pod Configuration for Miracast via Solstice Dashboard
Ethernet Only (recommended)
On the Network tab, enable Wireless Settings.
Select Attached to Existing Network radio button to enable wireless antenna for Miracast discovery and click Apply. Do not attach the wireless interface to an existing network. This interface remains idle and is used for the Miracast discovery stage.
On the Appearance and Usage tab, enable Miracast – Stream video over WiFi Direct and over Existing Network.
Warning
Turning Miracast Wi-Fi Direct off and back on in quick succession for a Solstice display may result in it temporarily appearing multiple times in Windows' Connect and Wi-Fi connection panels. To resolve this issue, refresh the list of available Miracast WFD devices on affected Windows devices by turning Wi-Fi off on and back on.
Wireless attached to existing network only
On the Appearance and Usage tab, enable Miracast – Stream video over Existing Network.
Ethernet + Wirelessly Attached to Existing Network
On the Appearance and Usage tab, enable Miracast – Stream video over Existing Network.
Ethernet + Wireless Access Point
Miracast not supported. When the Pod is acting as an access point, Miracast discovery cannot operate. Contact Mersive to discuss other options like attaching your Pod to an existing network.
Wireless Access Point Only
Click Apply to update the Pod with Miracast settings changes.
Related Topics
Next Topic
Miracast Performance Overview
Miracast is a standard for wireless connections from sending devices (such as laptops, tablets, or smartphones) to display receivers (such as TVs, monitors, or projectors), introduced in 2012 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It can roughly be described as "HDMI over Wi-Fi," replacing the cable from the device to the display.
The standards for Miracast are defined by the Wi-Fi Alliance, with significant contributions from Microsoft. It has similar functionality to AirPlay from Apple and Chromecast from Google. A variety of devices now natively support Miracast, including laptops running Windows 8.1 and 10, as well as devices from consumer companies such as Samsung, LG, Roku, and Amazon. Mersive introduced Miracast support starting with Solstice 3.5, and made improvements to Miracast connectivity, video and audio delivery, and latency in Solstice 4.6
Note
Android phones starting with version 4.2 were Miracast-enabled, but support was dropped at version 6.0.
Mersive's Miracast Support
Mersive’s implementation of Miracast fully complies with the Wi-Fi Alliance specification for Wi-Fi Direct (WFD) and the Miracast over Infrastructure Connection Establishment Protocol (used for the Existing Network implementation). It uses the following protocols:
Device discovery based on Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS), a peer-to-peer (P2P) protocol
A control protocol based on RTSP, layered on TCP
A streaming protocol based on RTP, layered on UDP
Mersive is one of very few vendors that support both WFD and Existing Network implementations. Furthermore, the Mersive’s Existing Network, or infrastructure mode, supports encryption which is critical in enterprise network deployments. Mersive’s implementation of Miracast also honors the use of default or “per Pod” encryption certificates.
Miracast Limitations
Miracast is based on UDP which does not guarantee data packet delivery. Consequently, Miracast connections are more sensitive to network stability. When compounded with wireless infrastructure limitations and environmental factors, Miracast performance may not be optimal. Mersive’s implementation avoids many of these issues as it is architected to be more resilient in dealing with environmental gaps. However, your Miracast performance also depends on the user device’s implementation of Miracast support. For the best performance and collaboration experience, Mersive always recommends using the Solstice app.
Technical Description
Miracast supports sharing over two different transport types:
Wi-Fi-Direct (WFD). A peer-to-peer (P2P) connection that does not require a wireless access point (WAP) where your client device connects in a single-hop to the synch device (i.e., the Solstice Pod). In this mode there is no need for any additional network infrastructure
Existing Network (or Miracast over Infrastructure). A connection over an existing Wi-Fi or Ethernet network using the “Miracast over Infrastructure Connection Establishment Protocol” (MS-MICE). Typically, the existing network is an internal LAN that can be either Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Process for Sharing with Miracast
Three steps need to be completed in the process of sharing content using Miracast on a Solstice Pod:
Device discovery of Miracast-enabled Solstice Pod (with Miracast enabled).
Authenticating to the Solstice Pod.
Sharing device content to the Solstice Pod over Miracast.
1. Device discovery of Miracast-enabled Solstice Pod (with Miracast enabled)
After Miracast is enabled, the Solstice Pod broadcasts that it supports Miracast along with some of its capabilities such as SSID, name of Pod, encryption method, infrastructure capability, etc. This is similar to how a Wi-Fi hotspot broadcasts SSIDs so you can connect.
This broadcast is the required method for devices to find the Miracast-enabled Pod to Miracast using either Wi-Fi Direct or Existing Network. It is even required even if you only use the Existing Network transport.
If you disable WFD in Solstice, it does not disable Wi-Fi Discovery broadcast as it is the only way to find the Pod. In this mode, essentially WFD connections are refused but Wi-Fi itself is still on.
2. Authenticating to the Solstice Pod
After device discovery, the IP addresses of the client device and Solstice Pod are passed to the protocol layers, which initiate a TCP connection which allows a capabilities exchange and session setup. This is followed by a UDP connection for video and audio streaming.
Additionally, the way the device connects to the Pod and how it authenticates, is different depending on whether the Solstice Pod is set up to use Wi-Fi Direct or Existing Network.
If the Pod is in Wi-Fi Direct mode, the device negotiates directly with the Pod via Wi-Fi and joins as a P2P group. If Access Control for the Pod has “Enable screen key” checked, the device authenticates via WPS. (This is functionality that the WPS button on your Wi-Fi router employs to connect devices). If “Enable screen key” is not checked, the device connects without authentication.
If the Pod is in Existing Network mode, the device negotiates and connects with network port (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and check to see if a screen key is required. If a screen key is required, then it encrypts traffic using Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS).
3. Sharing Device Content over Miracast
Audio and video are shared over Miracast using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP). You can have a maximum of four simultaneous Miracast session on a single Pod. However, depending on network bandwidth and latency, two Miracast sessions may be more practical.
Of course, all Miracast connections are concurrent with all other client connections to the Pod.
Miracast Performance Expectations by Use Case
The sections below describe the options for Miracast network configuration and discuss the setup and use of Solstice’s Miracast support to achieve the best possible performance.
Note
Both the Pod’s local configuration panel and the Solstice Dashboard allow the user to select a Miracast mode, or select both modes. For more information on how to configure Miracast, see Enable Sharing with Miracast.
Over Existing Network – Miracast via Ethernet
Miracast mode: Over Existing Network
Solstice Pod network connection: Attached via Ethernet
Client device network connection: Attached via Ethernet
This use case offers the highest reliability for Miracast sessions, with ~0% packet loss and >95% connection success. The latency should remain in the range 100-166ms, and corruption should be non-existent. If both Ethernet and Wi-Fi are enabled, Miracast favors Ethernet. This is the least common use case because it requires an Ethernet cable connection, which in most cases means the device is a laptop.
Over Existing Network – Miracast via Wireless Network
Miracast mode: Over Existing Network
Solstice Pod network connection: Attached wirelessly
Client device network connection: Attached wirelessly
The performance of this use case is entirely dependent on the performance of the existing wireless network. Problems such as distant access points or low signal strength can significantly decrease reliability and create packet loss as high as 10% and latency of multiple seconds.
Measuring signal strength of the existing wireless network is an important step in setting up this mode. Solstice Pods can internally measure signal strength, but this information is not available to users. Android phones and many other devices can measure Wi-Fi signal strength. Here is a table that lists expected performance based on signal strength:
Signal Strength | Signal Quality | Description |
|---|---|---|
> -30 dBm | Excellent | Maximum achievable signal strength |
> -50 dBm | Very Good | Excellent level for all network uses |
> -65 dBm | Good | Sufficient level for streaming video |
> -70 dBm | Marginal | Acceptable only for web browsing and email |
> -80 dBm | Poor | Packet delivery will be unreliable |
< -90 dBm | Very Poor | Mostly noise, not usable |
Over Existing Network – Miracast via Ethernet or Wireless Network
Miracast mode: Over Existing Network
Solstice Pod network connection: Attached via Ethernet or wirelessly
Client device network connection: Attached via Ethernet or wirelessly
The performance and latency of Miracast in this use case falls somewhere between that of Miracast via Ethernet and Miracast via Wireless Network, and is mostly determined by the quality of the wireless network, because Ethernet is highly reliable.
WiFi Direct – Miracast via WiFi Direct
Miracast mode: Stream video over Wi-Fi Direct
Solstice Pod network connection: No network connection required, but Pod must have Wireless Settings enabled and WAP disabled
Client device network connnection: No network connection required
This use case offers reasonable reliability for Miracast sessions, generally with <1% packet loss and >90% connection success. The latency should remain in the range 100-166ms, and corruption should be limited. Wi-Fi Direct works well because a link is made directly between the device and the Solstice Pod, thereby avoiding any performance issues with the enterprise wireless network. Wi-Fi Direct depends on the device and the Pod being within approximately 150-200 feet of each other, with mobile devices typically needing to be within a 25-35-foot range. This essentially means that the device and Pod need to be in the same room.
Other Important Considerations
The resolution of Miracast streaming is limited to 1080p.
Miracast beaconing (Wi-Fi Direct mode) occurs on the 2.4 GHz band on channels 1, 6, or 11.
Miracast streaming when in Wi-Fi Direct mode also occurs on the 2.4 GHz band on channels 1, 6, or 11. The reason is because Wi-Fi Direct mode does not use the 5 GHz band. Solstice cannot configure which channels Wi-Fi Direct uses.
If using Wi-Fi Direct, ensure that there is no channel overlap within your corporate wireless environment. If there is significant noise on the same channels that are used for Wi-Fi Direct, the user experience and performance may be significantly degraded.
Enable Sharing with AirPlay
Screen mirroring for Mac and iOS devices is available through Solstice's support for AirPlay® mirroring. This allows users to wirelessly stream their screen to the Solstice display in real-time without having to install an app. If your network does not allow UDP broadcast traffic or Apple's Bonjour protocol, Solstice provides an AirPlay discovery proxy alternative that can be used instead.
Network Routing Requirements
The following network ports/routes are required to support AirPlay streaming to Solstice Pods.
TCP ports 6000-7000, 7100, 47000, and 47010: Allow inbound AirPlay traffic to the Solstice host.
UDP port 5353: Required for iOS mirroring via the Bonjour protocol. It is not required when using the Solstice Bonjour Proxy.
UDP ports 6000-7000, and 7011: Allow inbound AirPlay traffic to the Solstice host.
Note
For more information on all of the network ports that Solstice uses, see Open Network Ports.Open Network Ports.