- Solstice Documentation
- Deploy Solstice
- Solstice Setup
- Network Requirements
Network Requirements
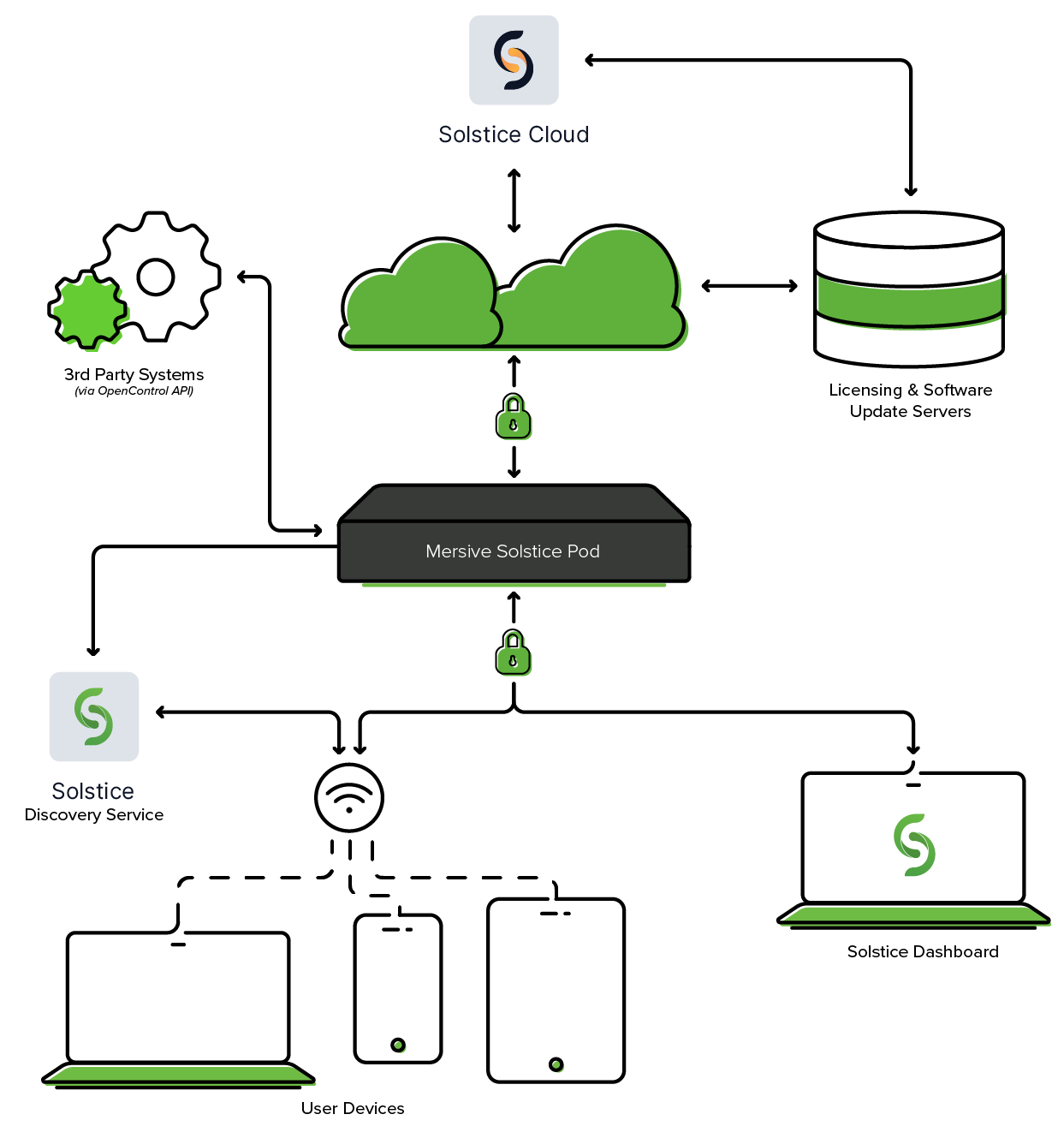
Solstice uses all TCP/IP standard network traffic to communicate across all the required and optional components of the Solstice system. The network(s) that Solstice is ultimately deployed on needs to allow peer-to-peer TCP connections. Additionally, for enterprise networks, firewall exceptions may need to be made and network ports may need to be open to allow certain Solstice capabilities to function.
Firewall Exceptions
URLs
You may also need to make firewall or proxy bypass exceptions for the following sites:
Required for software updates, Solstice Cloud, default RSS feed, default digital signage feed:
mersive.com*.mersive.com
Specific sites required for Solstice Cloud management (formerly known as Kepler):
kepler.mersive.comkepler-backend.mersive.comkepler-auth.mersive.comkepler-auth-svc.mersive.comkepler-onboarding.mersive.com
Required for pod activation, licensing, and subscription updates:
kepler-backend.mersive.com(Solstice 5.5.3 and Solstice 6+)manager.flexnetoperations.com(Solstice 5.5.2 and lower) - Retired Aug 15 2023
To detect captive portals, Solstice 6.0 and earlier may periodically attempt a connection to:
clients3.google.com/generate_204Note
Learn how to disable captive portal checks in Solstice versions 5.3 to 6.0.
Programs
Windows deployments using a tool that limits program access, like an anti-virus program, device management service, or a local firewall such as Windows Defender Firewall, may need to whitelist or allow the following program files used by the Mersive Solstice app on Windows:
rsusbipclient.exeSolsticeClient.exeSolsticeConference.exeSolsticeVirtualDisplay.exe(Mersive Solstice app 5.5.2 and earlier)
Tip
Windows installers for the Mersive Solstice app version 6 and later automatically add Windows Defender Firewall exceptions for rsusbipclient.exe and SolsticeClient.exe.
If the programs are not listed, add the programs manually using the installation path of the Mersive Solstice app. Example installation paths are as follows:
MSI & SCCM (installed with admin access from mersive.com/download/) app v5.3+ installers location:
C:\Program Files\Mersive Technologies, Inc\Solstice\Client
MSI Solstice Conference drivers (installed with admin access from mersive.com/download/) installer location:
C:\Program Files\Mersive Technologies, Inc\Solstice\Solstice Conference
Quick Connect app (installed with user access from v5.3–5.5.2 Solstice Pods or mersive.com/download/) location:
C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Local\Mersive\SolsticeClient
Open Network Ports
Depending on which features your end-users will use, certain network ports/routes must be open for Solstice to work correctly. Ports used for communication between a Solstice host (Pod) and Mersive Solstice user apps apply for both standard Solstice content sharing and Active Learning uses. Ports specific to Solstice conferencing video and audio sharing are identified below.
TCP
7: Used for gateway check. (Feature deprecated on Pods running Solstice version 5.3.2 and later.)
80, 443: Used if the Solstice host is allowed to connect to the internet for license activation and software upgrades. When pushing a local update file to the Pod, these ports need to be open between the Pod and the Dashboard. These ports are also used by the OpenControl API to interface with 3rd party systems. When network encryption is enabled, the Solstice Dashboard sends SLR updates via port 443.
Note
If you are using a Solstice Pod or Solstice Dashboard on 4.1 or later, communication to Mersive's license server only occurs over https/port 443.
1337: Used for integrating a personal Microsoft 365 calendar with the Mersive Solstice user app.
5443: Used to communicate with the Solstice OpenControl API, including setting passwords for Solstice Pods.
6443: Used for browser-based sharing connections.
7236: Miracast WiFi Direct control port used to establish and manage sessions between the source device and the Pod.
7250: Port on which the Pod listens for Miracast packets when Over Existing Network mode is enabled.
6000–7000, 7100, 47000, 47010: Should allow inbound AirPlay® traffic to the Solstice host.
53100, 53101, 53102: Used by default for basic communications between the Solstice host and end user devices, as well as Solstice Dashboard management. The base port (53100 by default) can be changed in the Network Settings of the Pod’s local configuration panel or Solstice Dashboard.
Important
Changing the Solstice base port for a Pod also changes the sequential streaming port (Solstice base port +1) and notification port (Solstice base port +2) used by Solstice. You must ensure that all three ports are opened on your network.
53103–53106, 53118, 53119: Used by Solstice video conferencing functions in addition to the default base ports 53100–53102.
TCP ports used for Windows devices: 53103, 53104, 53118, 53119.
TCP ports used for macOS devices: 53105, 53106.
Important
Changing the Solstice base port for a Pod also sequentially changes the ports Solstice uses to connect to video conferences. For example, if you change the configured Solstice base port to 53101, the ports used by the Solstice Conference drivers change to 53204–53220.
53200, 53201, 53202: Used by the Solstice host and end user devices to communicate the Solstice Discovery Service (SDS) host if SDS discovery mode is enabled.
Note
Browser-based sharing can use any non-privileged TCP port from 1024 to 65535. (Also see UDP port usage for browser-based sharing.)
UDP
123: Used to communicate with an NTP server.
5353: Required for iOS mirroring via the Bonjour protocol. It is not required when using the Solstice Bonjour Proxy. Also, if Miracast Over Existing Network mode is enabled, this port is used for multicast DNS (mDNS). mDNS is broadcast to the local subnet of each network interface the Pod is connected to. If the computer that is attempting to make an infrastructure connection is on a different subnet, this broadcast fails. If this happens, a workaround is to create a DNS entry to the Pod’s hostname.
6000–7000, 7011: Should allow inbound AirPlay® traffic to the Solstice host.
53107–53117: Used in Solstice video conference integration for audio and video routing. The base port (53100 by default) may be changed in the of the Pod’s local configuration panel or Solstice Dashboard.
Note
Important note: Changing the Solstice base port for a Pod also sequentially changes the ports used to share Solstice to a video conference. For example, if you change the configured Solstice base port to 53101, the video conference integration ports changes to 53208–53218.
For Solstice version 5.5 and later, see the table for more about UDP ports used by the Mersive Solstice app (client) and Solstice Pod (server) to connect Solstice to a video conference. Ephemeral source ports may be any port in the 1024–65535 range.
Client OS
Client Port
Server Port
User For
macOS
Ephemeral
53107
Video conference microphone audio
macOS
Ephemeral
53108
Video conference speaker audio
Windows
53110
Ephemeral
Video conference camera video
Windows
Ephemeral
53111
Video conference camera RTCP
Windows
53112
53112
Video conference microphone audio
Windows
53113
Ephemeral
Video conference microphone RTCP
Windows
Ephemeral
53114
Video conference microphone RTCP
Windows
Ephemeral
53115
Video conference speaker audio
Windows
Ephemeral
53116
Video conference speaker RTCP
Windows
53117
Ephemeral
Video conference speaker RTCP
55001: Used for display discovery if broadcast discovery mode is enabled.
Note
Both Miracast and browser-based sharing capabilities can use any non-privileged UDP port from 1024 to 65535. (Also see TCP port usage for browser-based sharing.)
Network Diagram